North Korea stores malware in blockchain smart contracts
North Korean hackers have started using EtherHiding, a blockchain-based technique, to distribute malware and steal cryptocurrency, according to Google's Threat Intelligence Group. The group identified as UNC5342 represents the first nation-state actor observed using this method.
Google traced the activity back to February 2025. The hackers use the "Contagious Interview" scheme, contacting developers in crypto and tech companies with fake job offers or collaboration proposals. When targets visit compromised websites, a small JavaScript loader executes and pulls malicious code from smart contracts deployed on BNB Smart Chain and Ethereum through read-only calls.
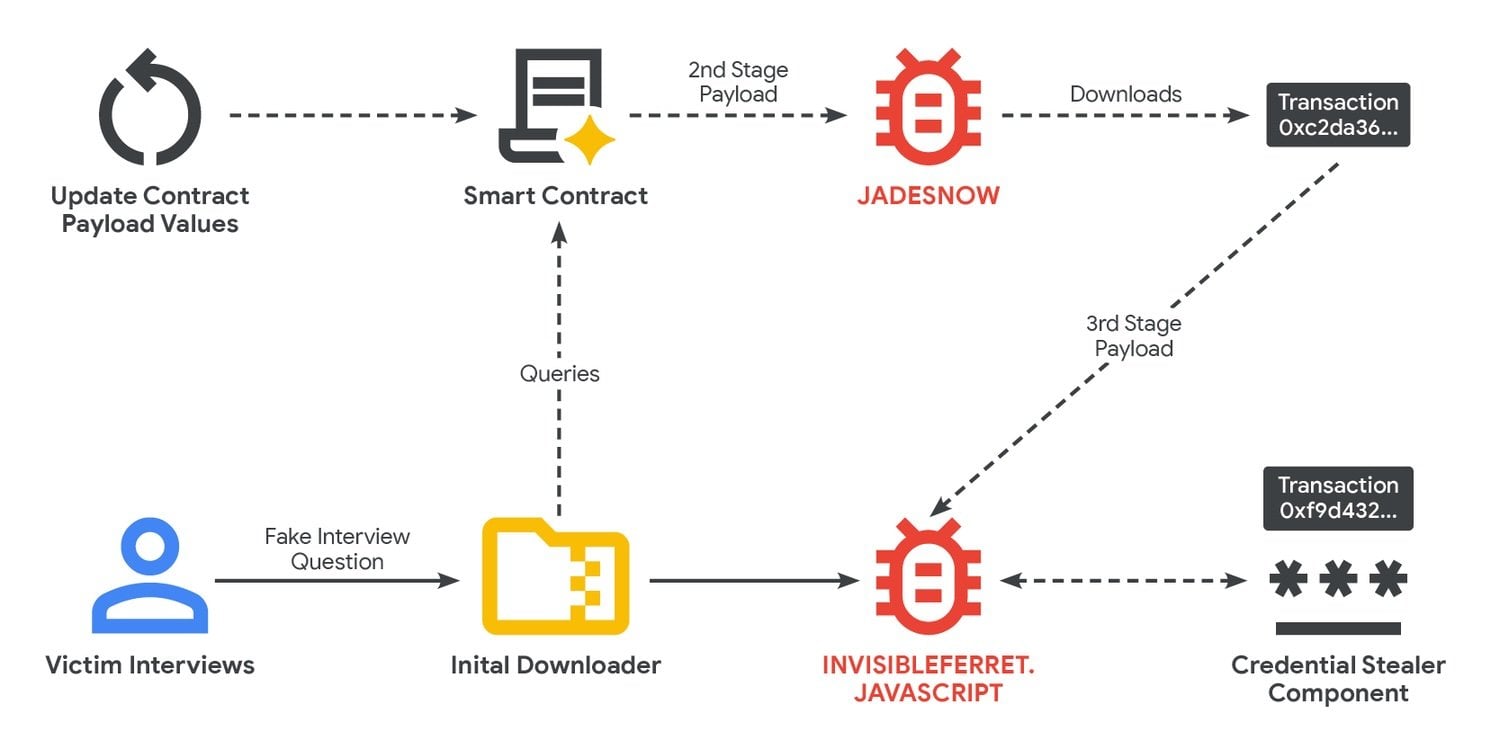
UNC5342 combines EtherHiding with standard North Korean tactics: fake recruiters, fabricated companies, and mock technical interviews. The goal is gaining access to developer systems to steal funds and compromise infrastructure.
The attack chain deploys two main tools: JADESNOW, a JavaScript downloader, and INVISIBLEFERRET, a backdoor. These programs steal login credentials and empty cryptocurrency wallets.
EtherHiding works by storing malicious code inside blockchain smart contracts. Once embedded in a contract, the code becomes difficult to remove. Attackers can update it while read-only queries leave no on-chain traces and cost nothing in transaction fees. The technique provides a persistent command-and-control channel that's harder to disrupt than traditional servers.

UNC5342 combines EtherHiding with standard North Korean tactics: fake recruiters, fabricated companies, and mock technical interviews. The goal is gaining access to developer systems to steal funds and compromise infrastructure.
Google provided specific indicators for security teams, including contract addresses on BNB Smart Chain and related Ethereum transactions. The company also documented a separate criminal group, UNC5142, using the same technique, showing that multiple threat actors now store malware on public blockchains.
EtherHiding first appeared in 2023 and 2024 in financially motivated campaigns, particularly through compromised WordPress sites displaying fake browser update prompts. UNC5342 adapted the technique for North Korean objectives, which include generating revenue through crypto theft and conducting espionage.
Google emphasized that the technique leverages public blockchain transactions to store and retrieve malicious payloads, giving attackers decentralization, stealth, and flexibility that traditional infrastructure cannot provide.
Recommended